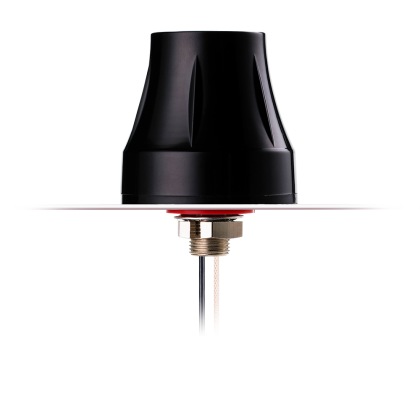
Antennas convert electrical signals to radio waves (and back), powering wireless links across industrial, commercial, and embedded systems. Online Components pairs dependable inventory with U.S.-based shipping, so qualified orders move quickly and purchasing stays predictable.
Our selection spans omnidirectional and directional styles, indoor and outdoor builds, and models covering the Megahertz to Gigahertz ranges. Key specs include standard 50-ohm impedance, stated Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) targets, and clearly listed frequency bands for straightforward matching.
How to Choose the Right Antennas
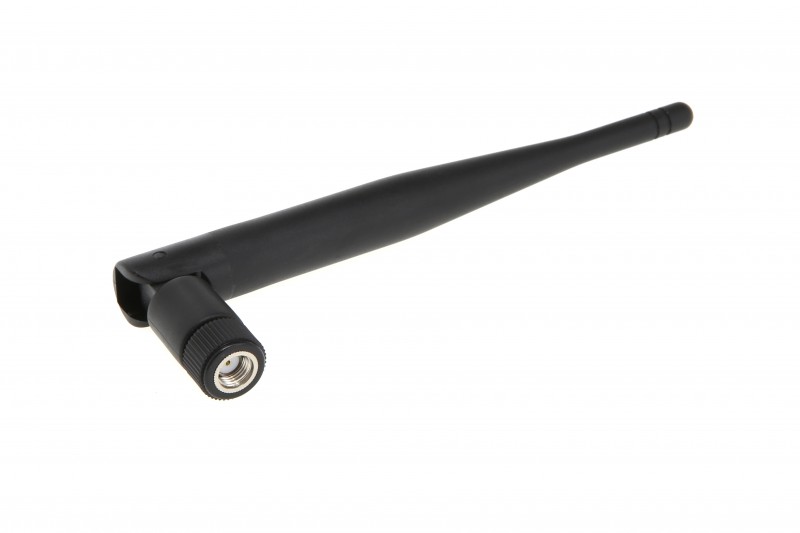
Start with frequency coverage and bandwidth. Next, match pattern and gain to your environment. Omnidirectional whips and low-profile forms give you broad area coverage. Higher-gain directional designs concentrate energy for longer links or busy RF spaces.
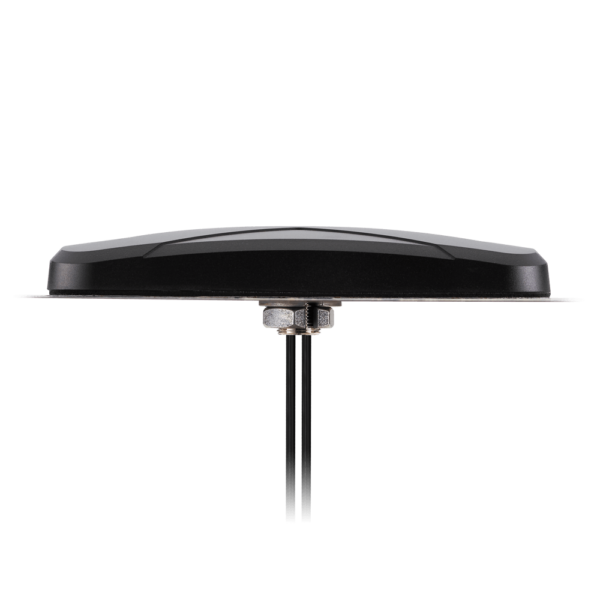
Then, confirm connector and mounting. You'll see SubMiniature version A (SMA), Reverse-Polarity SubMiniature version A (RP-SMA), and N-type interfaces often. Pole-mount, stud/New Motorola Mount (NMO) styles, and adhesive printed circuit board (PCB) trace antennas work for internal installs.
For outdoor duty or higher transmit levels, review polarization, power handling, and ingress protection.
Popular Applications for Antennas
Buyers and engineers source these antennas for production builds, field retrofits, and urgent replacements that keep lines running.
Manufacturing and logistics teams use sub-gigahertz or 2.4 gigahertz links for telemetry, asset tracking, and controls. Network and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) specialists deploy omnidirectional units for gateways and access points, or panel styles for point-to-multipoint links.
Transportation and field service crews rely on rugged mounts (NMO, pole-mount, or vandal-resistant housings) for vehicles and outdoor cabinets. Embedded product teams pick PCB trace antennas when internal space, adhesive mounting, and tuned 915 megahertz or 2.4 gigahertz performance matter most.
Why Buy Antennas from Online Components?
You get spec-accurate parts backed by supplier authentication, plus an ecommerce flow built for speed. U.S.-based inventory supports fast turnarounds with clear pricing and secure checkout.
Detailed data (frequency range, gain, pattern, connector, mount, polarization) helps you confirm compatibility before you buy, reducing sourcing time and risk. Standardizing across radios? You'll find multiband units that cover cellular, Wi-Fi, and other ranges in one footprint.
Antennas: What You Need to Know
What's the difference between omnidirectional and directional patterns?
Omnidirectional antennas radiate in a 360-degree horizontal pattern, perfect for broad coverage around equipment. Directional designs focus energy in a narrower beam to extend range or fight interference. Check gain and beamwidth on product pages to guide your selection.
Which connectors and mounts are commonly available?
SMA, RP-SMA, and N-type connectors are widely used, along with fixed, stud/NMO, pole-mount, and adhesive PCB formats. Picking the right interface cuts adapter loss and simplifies enclosure design.
How do I match antenna frequency to my radio?
Choose an antenna that covers your radio's operating band. Examples include 900 megahertz ISM, 2.4 gigahertz Wi-Fi, 5 gigahertz WLAN, and wideband cellular ranges (such as 698–960 megahertz and 1690–4200 megahertz). A proper match improves efficiency and return loss.
When should I use a PCB trace antenna versus an external whip?
Use PCB trace antennas for internal, space-constrained designs with controlled mechanics. Pick external whips or rugged mounts for higher gain, outdoor exposure, or quick field replacement without opening the enclosure.
Do polarization and power handling matter?
Yes. Matched polarization protects link budget, and adequate power handling supports reliability (especially outdoors or at higher transmit levels). Check both against your radio's plan.
contact us
 English
English
 Chinese
Chinese
 Italiano
Italiano
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 French
French
 Russian
Russian
 Japanese
Japanese
 Turkish
Turkish
 Korean
Korean
 Spanish
Spanish