As with most of our discussions about products and technology, we need to start with some background. In this case, what do we mean when we use the term “power supply”? A power supply, in the simplest sense, is a device that supplies electrical power to a load. It could be a battery, a generator, or something that plugs into an AC outlet.
More to our point, however, a power supply in the consumer and industrial sense usually means a device that takes AC power from a wall outlet, converts it to DC, changes the voltage to the amount required by the load, and finally supplies voltage to that load. Within that definition there are many power supply variations, including DC to DC converters, DC to AC inverters, linear suppliers, switchers, etc.
But our topic today is medical power supplies, and - are they really any different from regular power supplies? The answer to that question is an emphatic yes. Both types deliver electrical power, but medical power supplies answer to much higher demands for quality and performance.
What Drives the Difference in Medical Power Supplies?
As you might have guessed, any device or system that is used to diagnose or treat illness in people must offer a level of quality and performance that protects the patient. Not only does that make sense, it is also a dictum of the FDA. Many products and systems in the healthcare industry have electronic content and thus require a power supply.
Medical power supplies are designed to provide a conditioned output of electricity specifically for use with, or in products such as medical and surgical devices, imaging equipment, dental and dermatological equipment, and other health care devices. Power supplies in this category must be manufactured following the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60601 safety standard.
IEC60601: Product Safety Standards for Medical Devices is a series of technical standards that spell out the minimum safety and performance qualifications required of electrical equipment for professional medical use to monitor, diagnose, or treat a patient. The standard is accepted in the U.S., Europe, and Canada.
Since the patient is typically attached in some fashion to the medical equipment, the primary concern of the standard is isolation of the patient from potentially lethal voltages. It also addresses protection of the clinical staff who are operating the equipment. The standard delineates MOOP and MOPP certifications for power supplies. MOOP (Means of Operator Protection) covers reduced risk of electric shock to people other than the patient. MOPP (Means of Patient Protection) covers reduced risk of electric shock to the patient.

Parts of the IEC60601 standard also cover the type of electrical insulation that must be used in the power supply, the amount of safety barriers required, and the minimum isolation voltage which the supply can withstand. Isolation voltage is the ability of an insulator to minimize the flow of electric current with a high applied voltage.
The newest versions of the IEC60601 standard cover electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues for medical power supplies which may be exposed to, or generate electromagnetic interference (EMI) which may cause device malfunction and subsequent risk to the patient. Also, an additional standard, IEC61000, addresses power surges and voltage dips in medical power supplies, along with protection from RF interference.
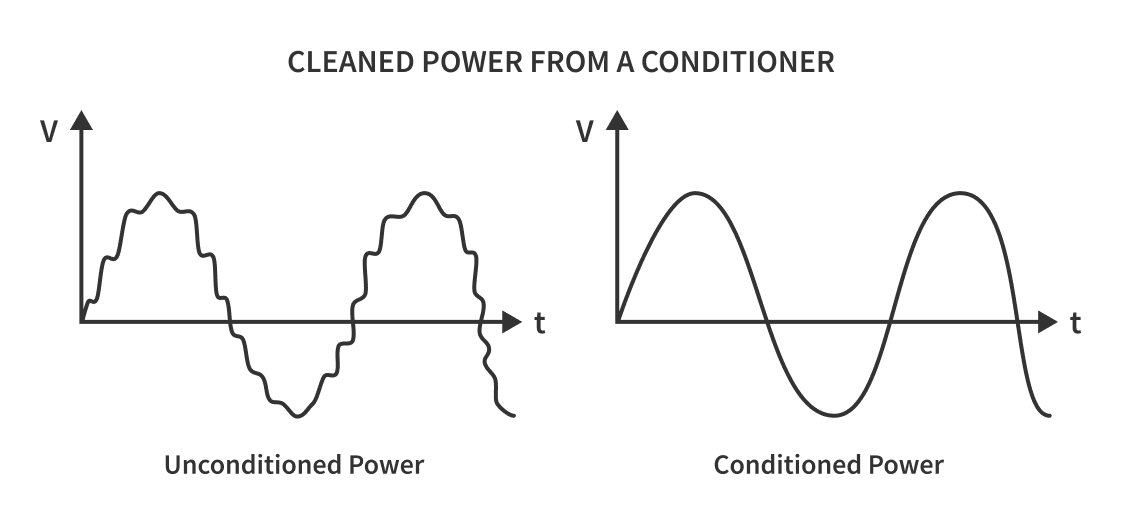
What is Conditioned Power?
Conditioned power from a power supply means that any voltage fluctuations in the output are smoothed out. Medical power supplies are regulated power supplies, offering stable voltage and current to power sensitive equipment, such as X-Ray, MRI, or CT scanners, which must be operated within strict power limitations. A voltage regulator circuit embedded in the power supply maintains voltage stability regardless of the amount of current consumed by the load.
Medical power supplies also manage ripple, which is the variations in voltage that may occur when the power supply is turned on. Any amount of ripple in certain medical devices can be a problem. Ripple is controlled in power supplies by the addition of smoothing capacitors in the device.
Medical Power Supplies – A Features Recap
As we can see, while medical power supplies basically provide power like any regular power supply, they also incorporate specific additional features and benefits that meet or exceed industry-accepted standards and regulations specifically covering medical devices, including:
- Voltage and current regulation for smooth electrical output
- Ripple reduction to protect sensitive equipment
- Significant input/output isolation to protect patients and staff
- Strict adherence to various industry safety standards
- Enhanced electrical isolation strategies
- Resistance to interference (EMI/RFI) from outside electrical devices
- Enhanced thermal and humidity resistance for hospital conditions
Summary
The most important feature of a medical power supply is that it provides multiple layers of protection for both the patient and the operator of the equipment being used. Additionally, these devices also provide the consistent and reliable power that is required for many medical devices and systems with sophisticated electronic content.
As with regular versions, medical power supplies are available in various package and mounting styles. Depending on their end use, they also come in specific or variable output ratings, and with different safety features to match applications that can vary from home medical devices to those used in a surgical theater setting. If you need help matching the correct medical power supply to your needs, you can reach out to the technical professionals at OnlineComponents.com by email at: TechSupport@onlinecomponents.com
If you are just learning about power supplies, or if you’d like to review your basic skills, you might check out our friends at CircuitBread.com. They offer tutorials and videos on both power electronics, and voltage and current sources on their website. You can check out their take on Medical vs Non-Medical Power Supplies here: Is there a difference between Medical and Non-Medical Power Supplies?
contact us:
 EN
EN
 English
English
 Chinese
Chinese
 Italiano
Italiano
 Portuguese
Portuguese
 Deutschland
Deutschland
 French
French
 Russian
Russian
 Japanese
Japanese
 Turkish
Turkish
 Korean
Korean
 Spanish
Spanish
 my account & orders
my account & orders


_450.jpeg)